SRN is happy to announce that it has added a new webpage to help CPST job seekers and employers connect with one another. From our website, find this resource under Resources/Job Postings for CPSTs.
News
Speeding a Trending Risk to Teens
GHSA Report: Speeding a Trending Risk to Teens
An analysis of recent crash data by the Governors Highway Safety Association (GHSA) has found that speeding is a factor in an outsized proportion of teen crash fatalities. In fact, from 2015 to 2019, speed was a factor in the deaths of more drivers and passengers ages 16 to 19 years of age (43%) than for all other age groups (average 30%). Read More from “Speeding a Trending Risk to Teens”
Special Needs Transportation Q&A
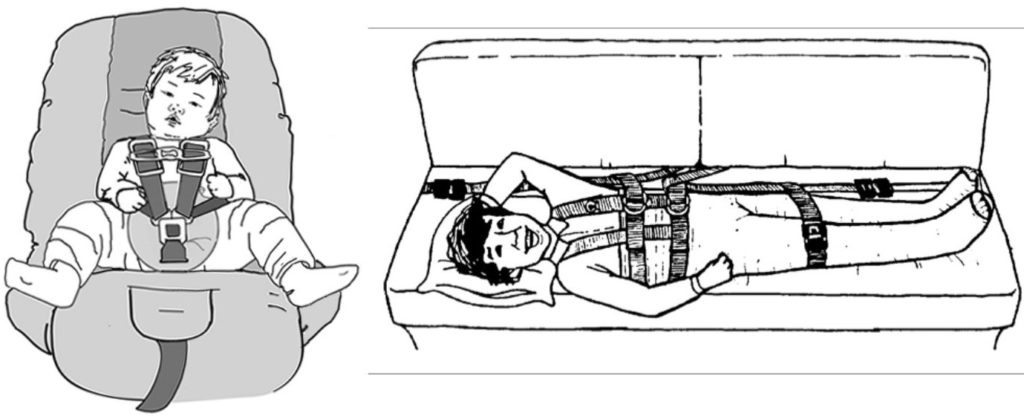
The Q&A format for this article was drawn from a conference webinar held in November, during which Barbara DiGirolamo of Boston Children’s Hospital reviewed the types of situations that arise when transporting children with special needs, as well as the CRs that are available to ensure these children continue to ride safely. DiGirolamo, a CPST-I and STAC (Safe Travel for All Children)-certified instructor, draws from her experience fitting children with a variety of special needs with suitable CR systems. Read More from “Special Needs Transportation Q&A”
Teens’ Vehicles Elevate Their Relative Risk
Vehicle Choice a More Serious Risk Factor for Teens Than for Other Drivers
Many of the studies on teen drivers, as well as policies and laws aimed at limiting various teen driving privileges, focus on characteristics of the teens themselves that are known to influence their safety in vehicles. However, the crashworthiness and crash-avoidance features of a vehicle are also important considerations for occupants of any age, and recent research shows that teens, as a group, tend to be at a disadvantage when it comes to benefiting from today’s safety features.
Read More from “Teens’ Vehicles Elevate Their Relative Risk”
Tips for Returning to In-Person Education
Virtual education has filled in many educational gaps during this year of pandemic, but some CPS programs are cautiously conducting in-person education, as well. Those that do must employ many new approaches in order to mitigate risk while ensuring quality of service.
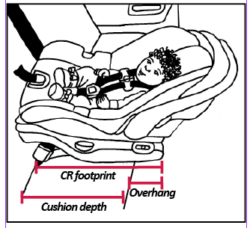
Is Your CR Hanging Out Too Much?
Understanding CR Overhang
The newly released version of the National CPS Certification Training curriculum does more than earlier versions to introduce the concept of overhang by including a slide and explanation in the technician guide. It tells students to ensure that the base (footprint) fits on the vehicle seat by checking the CR owner’s manual to learn about overhang, and it says to use the “80/20 guideline” if instructions don’t give other advice. It points out that some manufacturers require 100% of the footprint to rest on the vehicle cushion and that some vehicle seats are too shallow for some CRs. Read More from “Is Your CR Hanging Out Too Much?”
Virtual Education: Suddenly It’s All the Rage!
CPSTs are urged to continue conducting education remotely, using these helpful tips
While telephone support has been a tool used by CPSTs for decades to conduct remote education, most techs would agree that in-person education is far more thorough and effective. However, as the imperative for social distancing nixed all in-person interactions with caregivers this spring, virtual options, which incorporate both audio and video components, emerged as the next best thing. Almost overnight, individuals and programs across the country began transitioning from offering in-person outreach events, like checkups and classes, to hosting modified versions online. Read More from “Virtual Education: Suddenly It’s All the Rage!”
Refresher Course: Basic Guidelines for Cleaning CRs
Here are some basic CR cleaning guidelines. Of course, always refer to specific model instructions. However, these general recommendations can alert caregivers to the fact that, for important safety reasons, rules for cleaning a CR differ from rules for cleaning other items. These rules must be followed to maintain crashworthiness, even given heightened concerns about cleanliness during the COVID-19 crisis. Read More from “Refresher Course: Basic Guidelines for Cleaning CRs”
New School Bus Resource Defines Best Practice by Child Age
Safe Kids Worldwide recently compiled a best-practice document for CPS on school buses. Entitled Best Practice: Child Passenger Safety Securement Recommendations for Pre-School and School Age Children on School Buses, the document is laid out in a grid fashion. Rows list the child-age groups that signify distinct stages for CPS on school buses (starting with infants), while the columns give best-practice guidance, explanations/citations, and the rationale for distinguishing each child-age category.
Read More from “New School Bus Resource Defines Best Practice by Child Age”
Warning: Aftermarket LATCH = Fake LATCH

Fake CPS products are not limited to counterfeit CRs. The online availability of aftermarket LATCH systems is also a growing problem posing a danger to children. Multiple sellers are offering systems to add to CRs (LA attachment straps with connectors), as well as systems for vehicles (plates with LAs and TAs). When it comes to these aftermarket parts, no extra sleuthing is needed to conclude that they are unsafe: LATCH hardware should only be acquired directly from a vehicle or CR manufacturer. Read More from “Warning: Aftermarket LATCH = Fake LATCH”